The ScyllaDB team is pleased to announce the release of ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack 4.11.0
ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack is an open-source stack for monitoring ScyllaDB based on Prometheus and Grafana. ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack 4.11.0 supports:
- ScyllaDB 2024.1, 2024.2, 2025.1, 2025.2, and the upcoming 2025.3 release
- ScyllaDB Manager 3.x
This release includes multiple updates to the overview CQL, keyspace, alternator, manager, and advanced dashboards, including CPU Utilization, Alternator per-table panels, and others.
Related Links
- Download ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack 4.11.0
- ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack Docs
- Upgrade from ScyllaDB Monitoring 3.x to 4.y
- Upgrade from ScyllaDB Monitoring 4.x to 4.y
Version updates for ScyllaDB Monitoring Stack 4.11.0
- Prometheus upgraded to version 3.5.0
- Grafana upgraded to version 12.0.2-security-01
Grafana security updates 4.11.0
- The following Grafana Vulnerabilities fixes CVE-2025-6023, CVE-2025-6197, CVE-2025-3415
New Information in ScyllaDB Dashboards
Overview Dashboard Change
- Load stats to show User-Facing load #2003
The Load stats panel indicates how busy the CPU is. ScyllaDB uses a priority group mechanism to protect User-Facing activity from background activity.
Combining the load from User-Facing and background activity is misleading, as ScyllaDB utilizes periods of lower user activity for background operations like compaction and backup.
Instead, the load panel will now show CPU usage by User-Facing activity only.
- Node table shows disk usage #2551
The ‘Live’ column in the node table was hard to follow. Instead, in the case of a split-brain situation, the Status column will now display Split-Brain instead of Normal.
- Disk usage was added to the table; it shows disk usage as a percentile, meaning the percentage of total disk space currently used.
CQL Dashboard Change
- Add multi-partition BATCH gauge #2567
Using a multi-partition Logged BATCH is considered bad practice.
It provides weak atomicity guarantees and reduces performance, as the request is sent to a random node rather than the correct replica or shard.
A new gauge and graph have been added to the CQL Optimization section to indicate when a user is using a multi-partition Logged BATCH.
Keyspace Dashboard Change
- Enhance the Tables Table #2581
Multiple enhancements were made to the tables table, including adding units to values where applicable.
The table name now serves as a quick navigation link to that table.
New columns show the maximum reads and writes over the last 24 hours.
- Add keyspace table to the keyspace dashboard #2569
A new Keyspace Table shows a summary of all existing keyspaces.
It includes the number of tables and the number of active tables, meaning tables that were used in the last hour.
It also displays aggregated information about the tables in each keyspace, including disk size, reads, writes, and latencies.
The table is especially helpful in cases where the user maintains many unused keyspaces.
Alternator Dashboard Change
- Add Alternator per-table graphs #2559
Starting with ScyllaDB upcoming version 2025.3, Alternator includes per-table metrics.
The Alternator dashboard was updated to allow users to select a table and view the relevant operations specific to that table.
- Move the delete by TTL graph to be part of the cluster-wide section #2545
Manager Dashboard Change
- Add 1-1-restore metrics #2557
ScyllaDB Manager 3.6 adds the 1-1 Restore procedure, which restores an entire cluster that exactly matches the backup cluster.
New panels show the progress and remaining bytes of the restore procedure.
Advanced Dashboard Change
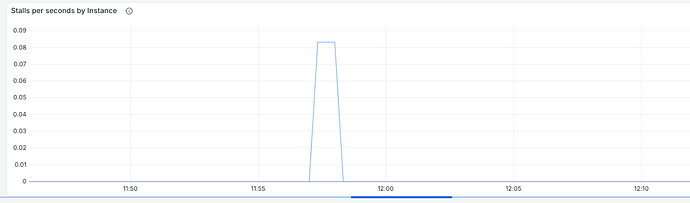
- Add Stalls Graph #2558
Stalls occur when a specific task runs continuously on the CPU without allowing other operations to execute.
The stalls graph is used by ScyllaDB support and engineers to identify potential issues.
Bug Fixes
- genconfig script fails to generate valid config with Scylla 2025 #2565
Operational Changes
- To prevent conflict with IPv6, Node name aliasing with genconfig.py is now configurable.
- Add an optional target for vector store. Vector Store is part of a future ScyllaDB Vector Search feature. #2580vv
- Presenting 20 most active Table`s in the keyspace dashboard #2564
The Keyspace Dashboard allows users to select which table to view. In cases where there are many tables, the dropdown can become too long to manage.
To address this, the dropdown now shows the top 20 most active tables based on reads and writes.
The updated Tables Table now also serves as a quick selection tool, allowing users to select a table by clicking its name.